Table of contents
The fascination with ancient ways of life often sparks curiosity about the hunter-gatherer lifestyle and its place in today’s world. As modern tourism continues to evolve, some travelers are drawn to experiences rooted in traditional survival skills and close connections with nature. This exploration delves into whether immersing oneself in hunter-gatherer cultures can be a viable and responsible tourism option, inviting readers to discover the complexities and ethical considerations of such adventures.
Understanding hunter-gatherer tourism
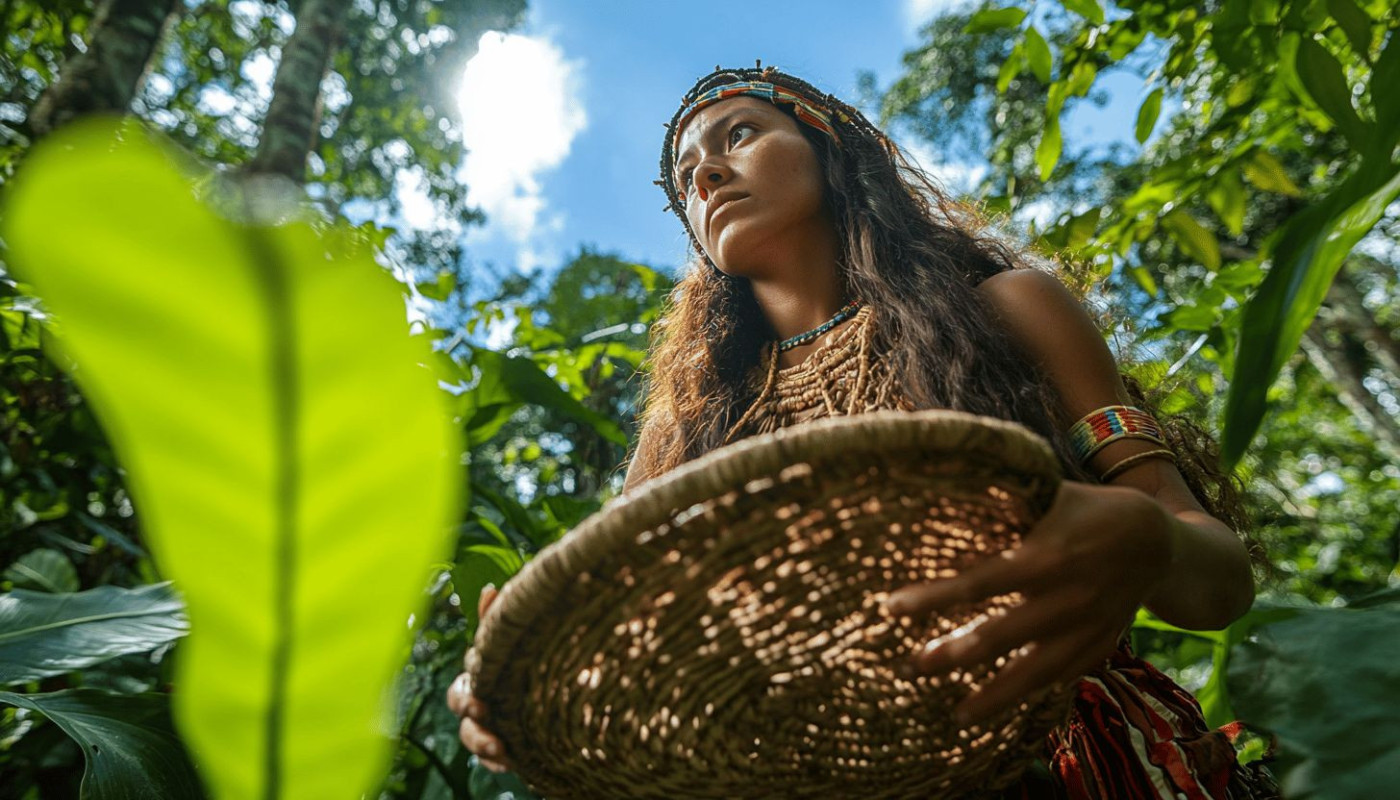
Hunter-gatherer tourism revolves around immersing travelers in the hunter-gatherer lifestyle, emphasizing ancestral skills such as foraging, fire-making, and crafting tools from natural materials. This unique form of immersive travel offers participants the chance to experience firsthand the subsistence strategy that sustained humanity for thousands of years, often guided by indigenous communities or trained experts. These experiences promote living in harmony with nature and deepen awareness of local ecosystems, often through eco-friendly tours that minimize environmental impact and respect traditional knowledge.
The appeal of hunter-gatherer tourism lies in its authenticity, drawing travelers who seek meaningful and educational encounters beyond typical sightseeing. Participants learn about ancient subsistence strategies, the cultural significance of wild foods, and the intricate balance between humans and their environment. As discerning travelers increasingly value sustainable tourism, options that focus on ancestral skills and low-impact living continue to gain traction, offering insight into resilient ways of life that predate modern agriculture.
With growing global interest in sustainable travel, destinations that offer well-structured hunter-gatherer experiences, such as guided walks with the Hadzabe people in Tanzania, have seen a rise in popularity. For those eager to engage in eco-friendly tours and enrich their understanding of indigenous cultures, the opportunity to go on a responsible safari adventure can be found at go, where visitors can explore authentic hunter-gatherer encounters in East Africa.
Assessing environmental impact
Hunter-gatherer tourism presents a unique set of environmental implications, as it often brings visitors directly into delicate natural habitats. On one hand, responsible travel initiatives can foster conservation awareness among tourists, encouraging them to respect wildlife and support preservation efforts. Such eco-tourism activities may provide economic incentives for local communities to maintain their environments, reinforcing the value of conservation and sustainable resource use. On the other hand, increased human presence risks exceeding the carrying capacity of ecosystems, potentially leading to habitat disturbance, wildlife displacement, and degradation of natural resources. To balance these outcomes, the integration of strict eco-tourism guidelines is vital, setting clear limits on visitor numbers and supporting ongoing environmental monitoring. By adhering to these practices, it becomes possible to minimize negative environmental impact while promoting the long-term health of natural habitats and encouraging ethical engagement with these unique environments.
Ethical considerations and cultural respect
When engaging in hunter-gatherer tourism, ethical tourism requires careful attention to the line between cultural appreciation and cultural commodification. Visitors, while eager to learn, must be aware that replicating indigenous traditions without proper context or consent risks eroding cultural respect and infringing on indigenous rights. Responsible tourism initiatives prioritize genuine community engagement, ensuring that local voices guide the design and delivery of experiences, rather than rendering ancient customs as mere attractions. Where community members are empowered to share their way of life on their own terms, tourism can support cultural preservation and local autonomy. Conversely, unchecked tourism may marginalize traditional knowledge keepers and reduce cultural expressions to performances for outsiders, leading to disenfranchisement. The adoption of transparent agreements, respect for customary protocols, and ongoing consultation with indigenous stakeholders form a foundational approach to balancing visitor interest with respect for indigenous rights, laying the groundwork for a more ethical and sustainable exchange.
Economic sustainability for local communities
Hunter-gatherer tourism offers new avenues for livelihood diversification, giving local communities a sustainable income that can reduce reliance on traditional sources such as hunting, fishing, or subsistence farming. By attracting travelers interested in authentic cultural experiences, fair tourism practices can ensure that tourism benefits reach a broader segment of the population, supporting education, healthcare, and community infrastructure. Economic sustainability depends on transparent revenue-sharing systems and capacity-building programs that empower communities to manage tourism ventures and retain control over their resources.
Despite these opportunities, there are notable challenges. Tourism initiatives may inadvertently foster dependency on external visitors, leaving local communities vulnerable to market fluctuations and seasonal downturns. In the absence of equitable governance structures, profits may be distributed unevenly, exacerbating social inequalities or even leading to conflicts within groups. For hunter-gatherer tourism to truly advance economic sustainability, it must continually balance the promise of sustainable income with the need for fair tourism models that prioritize local participation and decision-making, ensuring that the positive impacts are widely and fairly shared.
Balancing authenticity and visitor experience
Achieving interpretive authenticity in cultural tourism involving hunter-gatherer communities remains a challenge, as organizers must carefully navigate the line between providing authentic experiences and avoiding contrived spectacles. For visitors seeking meaningful travel, genuine engagement with local customs, daily activities, and storytelling creates lasting value while promoting heritage preservation. To foster visitor satisfaction without compromising community dignity, tourism programs can incorporate immersive activities guided by members of the community, open discussions about traditions, and opportunities to observe rather than intrude upon daily life. Additionally, transparent communication about the boundaries of participation and respect for sacred or private practices ensures that both hosts and guests benefit from positive, respectful encounters.
Best practices in this context involve establishing collaborative frameworks where community members actively shape the content and structure of tours, ensuring that their voices are central in the representation of their heritage. Equipping guides with training in interpretive authenticity can help avoid the pitfalls of staged or superficial encounters, supporting the integrity of the experience. Such an approach not only enriches the value of cultural tourism for visitors but also contributes to the preservation and appreciation of unique traditions within hunter-gatherer societies. In sum, prioritizing authentic experiences grounded in mutual respect and collaboration can transform tourism into a tool for both meaningful travel and sustainable heritage preservation.
On the same subject

Exploring The Charms And History Of Small French Communes

How To Plan An Unforgettable Cultural Journey?

Early Booking Benefits For A Stress-free Vacation
Nice car tour : a romantic idea you’ll never forget !

Exploring The Perks Of Cultural Exchange Programs In China

How To Choose The Right Yacht For Your Sailing Adventure

Choosing The Right Gear For Mountain Sports: Skis, Snowboards, And Bikes

Stunning lagoon view location in Sint Maarten at The Hills Residence

Exploring The Benefits Of Seasonal Camping On Mediterranean Coasts

